Project Description
Abstract:
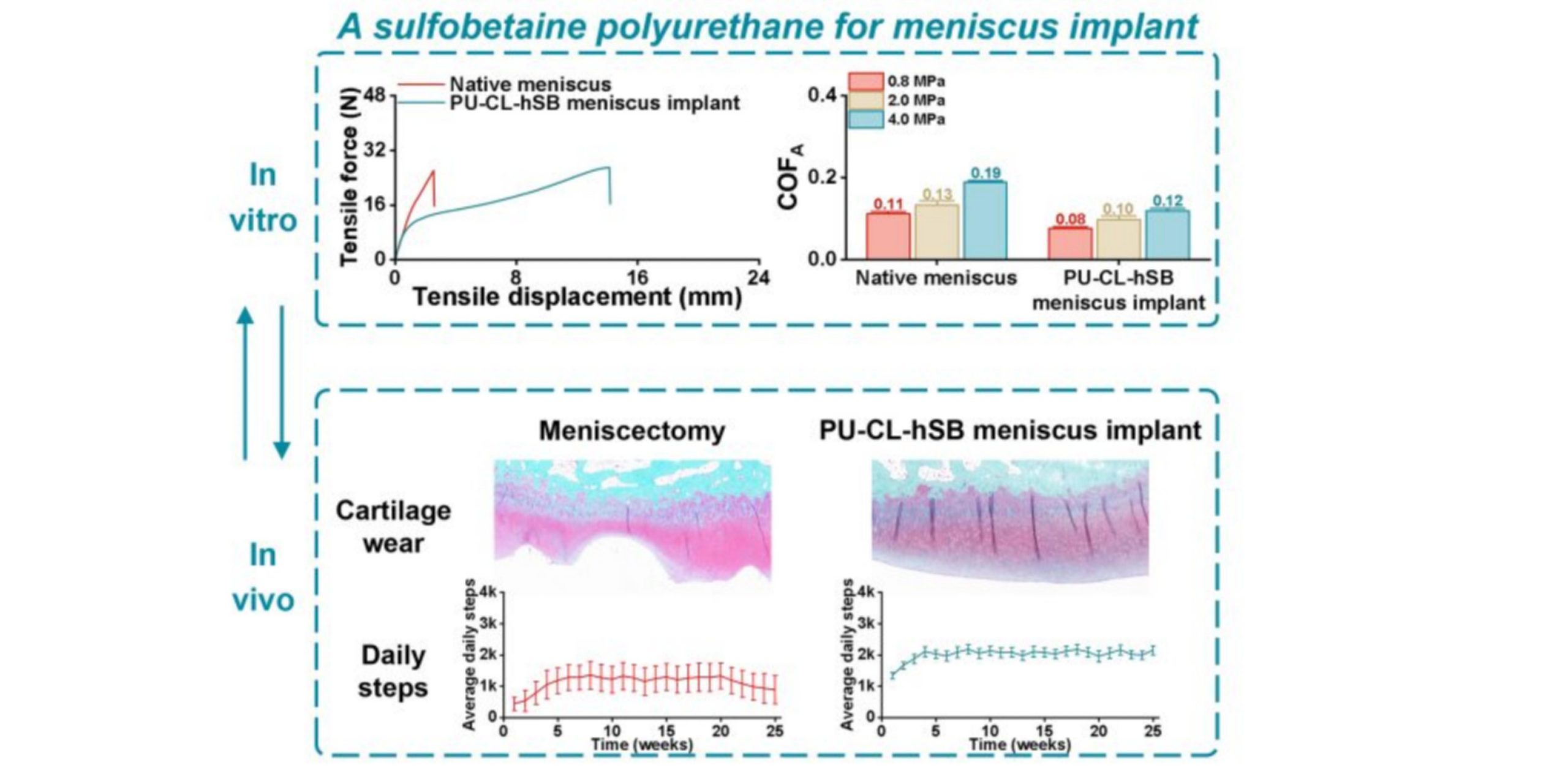
The development of substitutable meniscus implants that can effectively protect articular cartilage remains a great challenge. Herein, a polyurethane with chemical crosslinking and sulfobetaine extenders containing hydrophobic chains (PU-CL-hSB) is developed, which could improve comprehensive properties and long-term stability simultaneously. By regulating the mole ratio of functional groups, PU-CL-hSB with appropriate mechanical properties, excellent tribological properties, and good fatigue resistance is used to prepare substitutable meniscus implant by hot-pressing. Due to the synergistic effect of functional groups, PU-CL-hSB meniscus implant presents comparable or even superior properties to native meniscus. It withstands a maximum force of 26.08 N versus 25.14 N for native meniscus, an energy dissipation from 45.93 N mm to 39.17 N mm compared to 28.83 N mm to 19.11 N mm for native meniscus over 300 cycles, and a friction coefficient from 0.08 to 0.19 compared to 0.11 to 0.26 for native meniscus. This PU-CL-hSB meniscus implant is further implanted into live rabbit knee joints for 8 and 25 weeks by a new approach, and in vivo data indicate that PU-CL-hSB meniscus implant not only protects articular cartilage from severe damage without eliciting inflammatory responses, but also can maintain normal physiological activities in the native state. Our findings present a substitutable meniscus implant that could be applied in vivo and propose evaluation methodologies for meniscus implants.